|
Trigonodes
hyppasia Cramer
Noctua
hyppasia Cramer, [1779] 1782, Uitlandsche Kapellen,
3: 99.
Phalaena
deliana Stoll, 1790, Uitlandsche Kapellen,
5: 160.
Ophiusa
anfractuosa Boisduval, 1833, Fauna entomologique de Madagascar,
Bourbon et Maurice, Lep: 104.
Trigonodes
acutata Guen�e, 1852, Hist. Nat. Insectes, Spec. g�n. L�pid.
7:
283.
Trigonodes
exportata Guen�e, 1852, Hist. Nat. Insectes, Spec. g�n. L�pid.
7:
284.
Trigonodes
inacuta Guen�e, 1852, Hist. Nat. Insectes, Spec. g�n. L�pid.
7:
284.
Trigonodes
compar Walker,
1858, List
Specimens lepid. Insects Colln Br. Mus., 14: 1451.
Trigonodes
hyppasia Cramer; Holloway, 1976: 31; Kobes, 1985: 47.
|

Trigonodes
hyppasia 
(Andamans)
|
 |
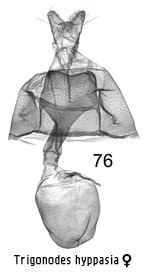 |
Diagnosis.
This and the next species have the centre of the forewing marked with two
pale-edged blackish triangles that together form a triangle. In hyppasia,
a smaller species, the more basal triangle is the larger, rather than vice
versa, and there are darker markings in the much broader marginal grey-brown
zone.
Geographical
range. Old World tropics and subtropics east to Fiji and Tonga.
Habitat
preference. Records are from disturbed forest and areas of secondary
vegetation and cultivation from the coast to 1050m.
Biology.
The larva was illustrated by Common (1990) and Miyahara (2001), and also
described by Sevastopulo (1941a, 1942). The upper half is yellow, the ventral
part browner. The yellow part is broken by longitudinal brown bands that become
fainter towards the posterior, but intensify again beyond the prolegs, which are
restricted to A5 and A6. Sevastopulo indicated that these bands are made up of
lavender and purple-brown lines, but their colour and composition is variable.
The body is slender.
Sevastopulo
described the egg as spherical with ribs, olive green, speckled rusty red. The
hatchlings are slender with yellowish brown heads and brownish green bodies.
Intermediate instars are green with three lateral purple brown lines. The pupa
is in a slight cocoon of white silk, spun amongst leaves.
The host
plants recorded (Common, 1990; Miyahara, 2001; Robinson et
al.,
2001) are mainly in the Gramineae (e.g. Chrysopogon,
Eleusine)
and the Leguminosae (e.g. Glycine, Indigofera,
Kummerovia,
Medicago, Phaseolus, Rhynchosia),
but there is also a record of Nephelium (Sapindaceae; Kuroko & Lewvanich, 1993).
<<Back
>>Forward <<Return to Content Page
|

