|
Lebeda cognata
Grunberg
Lebeda cognata
Grunberg, 1913, Ent. Rundsch., 30:103.
Lebeda cognata
Grunberg; Holloway, 1976: 89; Lajonquière, 1979: 691; Barlow, 1982: 50
|

Lebeda cognata
♂
(.85
natural size)

Lebeda cognata
♀
(.85
natural size)
|
|
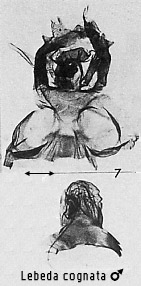
Diagnosis. The
striking two-tone ground colour of the forewing is distinctive in the male, and
the course of the curved boundary of the two zones is faintly evident in the
female; the female is distinguished from the next two species in being larger
and having a crescent-shaped white discal spot.
Taxonomic notes.
The species agnata Tams from Peninsular Malaysia is smaller and darker overall
in the male. The Himalayan and Chinese nobilis Walker extends to Peninsular
Malaysia, Sumatra and Java but has the forewing dark zone restricted to a
diffuse streak through the discal spot by a pale lens-shaped area along the
costa.
Geographical
range. Borneo, Peninsular Malaysia, Sumatra.
Habitat
preference. The species is frequent in lowland rainforest.
Biology. L.
nobilis is polyphagous on dicotyledonous trees and conifers and has been noted
especially from genera of economic importance such as Pinus (Pinaceae) and Quercus
(Fagaceae).
L. cognata is likely to have a similarly wide range of diet, but was noted
from Trema
(Urticaceae), Citrus (Rutaceae) and Rosa (Rosaceae).
The fully grown
larva was illustrated by Barlow (1982). It is a pale ashy grey with darker grey
reticulation, the lateral protruberances being adorned with hair-like and
spatulate setae of pale grey. The meso- and metathorax have transverse ridges
of black setae, that of the metathorax larger. Early instars are black, scarlet and
white with black hair pencils, and middle instars are dark brown.
<<Back
>>Forward <<Return to Contents page
|

