|
Macroglossum insipida Butler
Macroglossa insipida Butler, 1875, Proc. zool. Soc. Lond., 1875: 12.
Macroglossum insipida Butler; Rothschild & Jordan, 1903: 642.
|

Macroglossum insipida ♀
(.85
natural size)
|
|
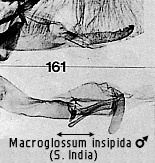 |
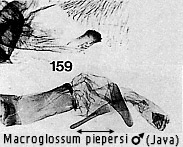
Diagnosis and taxonomic notes. The species is easily confused with M.
troglodytus Boisduval and M. pyrrhosticta Butler, similarly wide ranging
species that have yet to be recorded reliably from Borneo. They occur in
Sumatra (Diehl, 1980) and Java (Dupont & Roepke, 1941) with M.
piepersi Dupont, a more localised species. The first two have a bifid
harpe on the valve, the upper portion either coarsely (pyrrhosticta) or
finely (troglodytus) serrate; M. piepersi has an undivided harpe that is
apically spatulate, finely serrate. The next species is also
likely to be confused and is distinguished in the description thereof
below. Other species occurring in Java and Sumatra that might be found in
Borneo and are externally similar are ungues Rothschild & Jordan (also
Philippines, Sulawesi, Moluccas) and sitiene Walker (mainland Asia to
Java, Philippines); they are probably sister-species, both having a
needle-like harpe on the valve of the male genitalia and a bifurcate
apical process to the aedeagus. M. variegatum can also be confused with
this group, but is distinguished by the short, acute, spinose harpe of the
male valve.
Geographical
range. Indo-Australian tropics east to Australia.
Habitat preference. The three specimens seen are from the lowlands.
Biology. The larva was described by Bell & Scott (1937) and Dupont
& Roepke (1941). Young larvae are green, speckled pale yellow, with
median and dorsolateral white lines and, laterally, white oblique stripes.
The fully grown larvae are more variable, with brown-marked yellow ones
and black-marked brown ones as well as green ones. The horn is basally
black, distally orange.
Recorded host-plants are: Borreria, Spermacoce (Rubiaceae); Corchoras
(Tiliaceae).
<<Back
>>Forward <<Return
to Contents page
|

